JOE MAKES
▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒▒
VAULT

What is VAULT?
VAULT is a fast command line utility for securely storing and retrieving user account information.
VAULT makes retrieving passwords as simple as:
$ vault github #Type vault account-name
MASTER PASSWORD --> supersecretpassword! #Enter the master password
github #Get your account information!
USERNAME --> jkerman
PASSWORD --> munorbust!How do I set this up?
Linux/MacOS
- Install Python 3.6 and “pycrypto” package
- Download the files in this repository to your computer (ie.
~/GitHub/vault) - Add vault shell script to
~/.bin - Add
export PATH=$PATH":$HOME/.bin"to.bash_profileor.bash_rcfile - In
vault.pyupdate “path” variable to point at passwords.json
Windows
- Install Python 3.6 and “pycrypto” package
- Download the files in this repository to your computer (ie.
Username/GitHub/vault) - Add vault.bat script to
C:\Users\Username - Edit vault.bat path to point at
vault.py - In
vault.pyupdate “path” variable to point atpasswords.json
How do I use this?
After getting setup - type “vault” into a terminal window. This will return the following:
-a will add a new account
-r will remove an existing account
-u will update information of an existing account
-g will get information for an existing account
-l will list information for all accounts
-h displays this help dialogI’ve included example account information in passwords.json for playing around with VAULT and seeing how it works. I recommend removing existing entries with “-remove” before adding any new account information.
NOTE using more than one “Master Password” will work for all functions except “-list” but is not recommended.
For example to add and account enter:
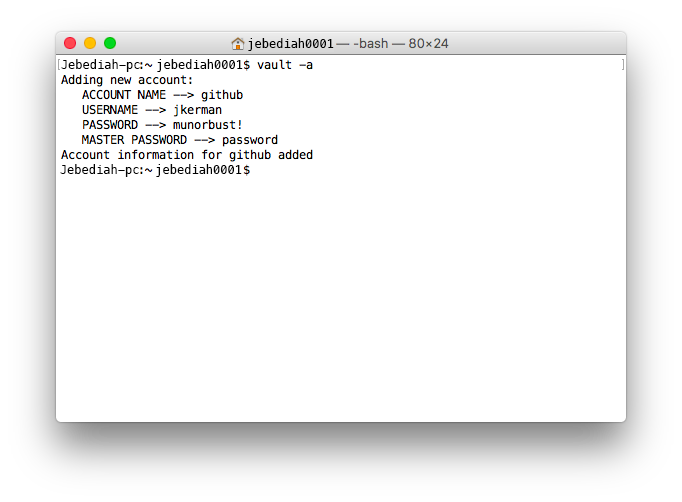
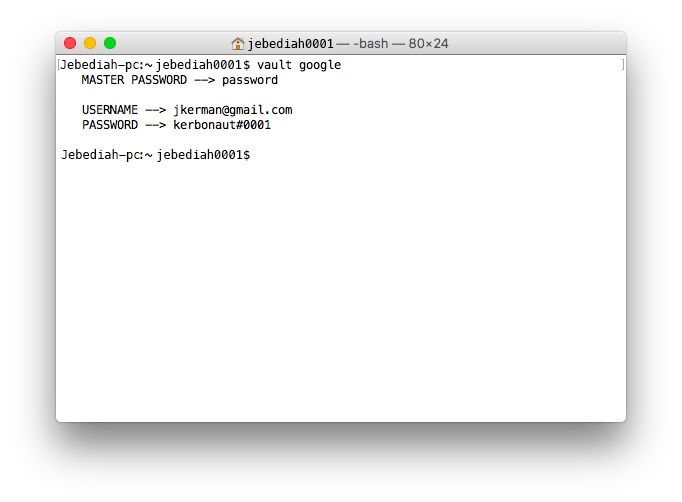
For faster access to account info enter “vault accountName”.
Can I sync my passwords across computers?
Sure! Do you have a folder backed up by Google Drive, OneDrive, Dropbox or another cloud storage service? Add passwords.json to this folder and edit the path in vault.py to point to this new location. When you make edits Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive etc. will sync the latest version across your connected devices and back it up to the cloud.
Is this safe?
“10/10 Cryptologists say it’s better than plaintext!”
Seriously though, I’m not an encryption expert so please use this this software at you own risk. The password encryption algorithems come from the “pycrypto” package for python.
Passwords are encrypted using an AES cipher with 32 character key (generated on-the-fly) and unique IV. This means the key is not stored on your computer, it’s generated from user input upon encrypt/decrypt actions - then forgotten. Anything BUT the correct master password will generate the wrong key and encrypt/decrypt will throw errors or return gibberish.
For more information on the AES cipher see –> https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Encryption_Standard
Site generated 2024-09-20